News
EIA: Electrolyzers are a small but growing source of U.S. H2 production
Developers in the U.S. have plans to expand H2 production using technologies that make use of electricity, an early sign that H2 production could move away from its current reliance on hydrocarbon feedstocks in the coming years.
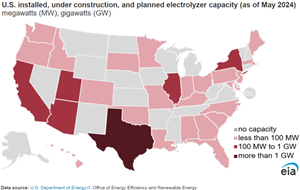
Planned electrolyzer installations that use electricity to produce H2 from water, if built, would expand capacity in the U.S. from 116 megawatts (MW) of current capacity to 4,524 MW, according to information collected by the U.S. Department of Energy’s H2 Program Record. If all the planned projects are implemented, U.S. production of H2 through electrolysis could total about 720,000 metric tpy compared with the current 10 MMt of H2 currently produced from fossil fuels and as a byproduct from other industrial sources. Electrolyzers that meet a threshold for low carbon intensity could qualify for a production tax credit if developers begin construction by 2033.
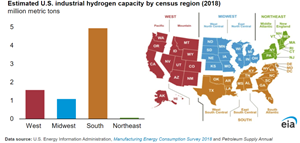
H2 is a critical input for petroleum refining and fertilizer production, and it can also be used as a storable fuel for electric power generation to be used in H2 gas turbines or blended with natural gas for use in traditional gas turbines. It is the simplest element found naturally on earth and is traditionally separated out of hydrocarbons, such as natural gas and coal, through a process known as steam methane reforming (SMR). The 10 MMtpy of H2 produced in the U.S. is almost completely supplied by SMRs or produced as byproduct H2 obtained from a chemical plant or other facility where H2 is not the main product. Using our Manufacturing Energy Consumption Survey 2018—the most recent year for which we have data—and our Annual Refinery Capacity Report, we estimate current U.S. SMR capacity totals 7.6 MMtpy of H2.
We are currently developing a new H2 supply model and adjusting consumption models to better incorporate H2 projections in our Annual Energy Outlook for 2025. We will host a working group discussion with stakeholders on June 12, 2024.
Electrolyzers vs. SMR. Electrolyzers produce H2 through electrolysis, a process that separates H2 from water using an electrical current, with oxygen as the only byproduct. Because SMRs use hydrocarbons as feedstock, their byproducts include carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide (CO2), which must be captured and sequestered to achieve net-zero emissions. H2 produced by electrolyzers is considered carbon-neutral if the electricity consumed is generated from renewable resources.
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), two types of electrolyzer technologies are currently commercially deployed, both of which require further improvements to stay competitive: proton exchange membrane (PEM) and alkaline. These technologies vary by construction cost, start-up times, and materials used to convert electricity to H2. No matter the materials used, electrolyzers can leverage electricity generated from renewable resources.
Although several electrolyzer projects are planned in the U.S., traditional SMR technology produces most of the H2 commercially consumed in the U.S. today.
The SMR process applies high-temperature steam to methane and a catalyst to produce H2, carbon monoxide, and carbon dioxide. Industrial facilities and petroleum refineries primarily use natural gas as the source of methane for H2 production. SMR units can be fitted with carbon capture and storage (CCS) capabilities to reduce the carbon footprint of H2 production by storing CO2 underground. This technology is not new; since 2013, the Coffeyville Resources Nitrogen Fertilizers plant in Oklahoma has been capturing CO2 created by H2 production and delivering it for enhanced oil recovery.